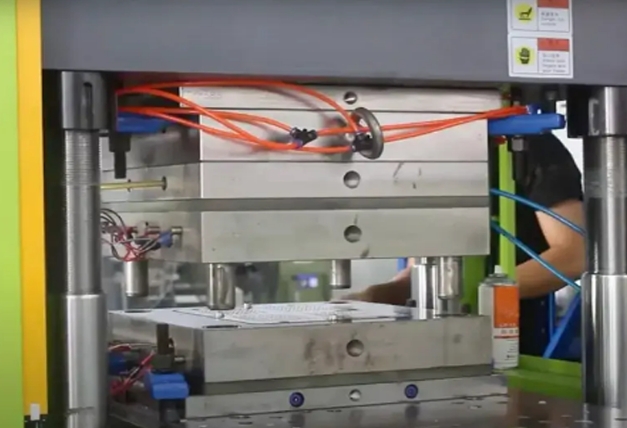
Compression Molding Service
- Time:2025-06-27
- Source:创始人
What is Compression Moulding?
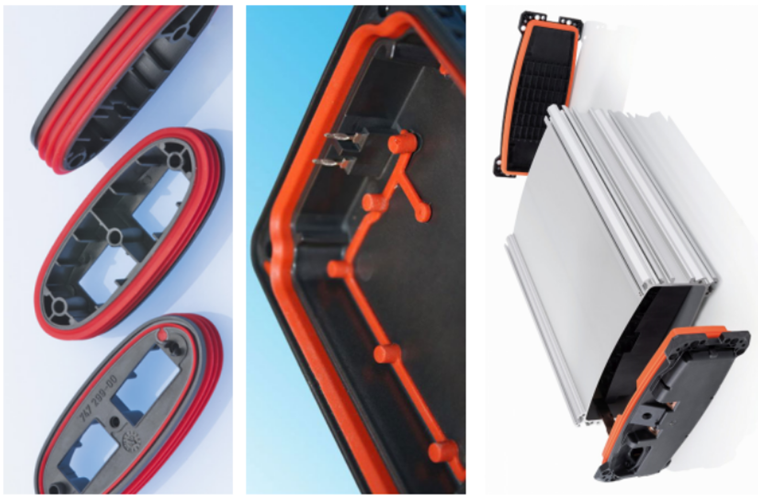
Compression molding service is a versatile and cost-effective process used to create durable, high-precision plastic and rubber parts. It involves placing a pre-measured amount of silicone into an open mold cavity, then applying heat and pressure to cure the material into the desired shape. This method is ideal for producing components like seals, gaskets, and custom silicone molding products.
The process’s success relies on carefully controlling factors like temperature, pressure, and material composition. Silicone compression moulding offers cost efficiency and minimal material waste, especially for low to medium production volumes. It is commonly used in industries such as medical, automotive, and consumer goods for high-precision parts manufacturing. Compared to other techniques like silicone injection molding, silicone compression molding stands out for its ability to handle complex shapes while maintaining consistency and quality.

Compression Moulding Materials
In compression molding process, thermosetting plastics, rubber, and composite materials are commonly used due to their ability to undergo a curing process and achieve a stable, rigid form. The selection of materials depends on the desired characteristics of the final molded products.
Common Rubber Compatibility Chart

Rubber is material that has been broadly exploited in compression molding mainly due to its design flexibility and exceptional sealing capabilities. Rubber exists in varying forms and some of these forms do not generate desirable results when processed using compression molding. Specialized rubbers such as silicone and elastomeric compound rubbers stand out in compression molding.
· Silicone Rubber: This unique rubber type is primarily utilized to manufacture components for food machinery and medical devices. This is because silicone rubber promises chemical inactivity and can withstand extreme temperatures.
· Elastomeric Compound Rubber: These include EPDM and nitrile rubber and they are mainly characterized by exceptional flexibility. Additionally, these types of rubber are oil and fuel tolerant making them perfect for manufacturing vibration dampeners and gaskets.
Additives Are Used in Silicone
Silicone additives come in various forms, that are added to silicone rubber to improve its properties or performance.
Some of the most common silicone additives include:
l Reinforcing Fillers: Reinforcing fillers are one of the most common types of additives. They improve the mechanical properties of silicone, such as tensile strength and tear resistance. These fillers, often made from silica, provide the silicone with the necessary toughness to withstand physical stress in demanding applications.
l Thermal Stabilizers: For applications exposed to high temperatures, thermal stabilizers are essential. These additives help maintain the thermal stability of silicone, ensuring it retains its properties even under extreme heat. This is particularly important in industries like automotive and electronics, where materials are frequently exposed to high temperatures.
l Flame Retardants: In scenarios where fire resistance is crucial, flame retardants are added to silicone. These additives reduce the material’s flammability, helping to prevent the spread of flames in case of fire. Flame retardants are commonly used in building materials, electronics, and transportation sectors to enhance safety.
l Plasticizers: Plasticizers are used to increase the flexibility of silicone. These additives lower the glass transition temperature of the silicone, making it softer and more pliable. This is particularly useful in applications where the material needs to flex or bend without cracking, such as in medical devices or consumer products.
l UV Stabilizers: For outdoor applications, UV stabilizers are added to protect silicone from the damaging effects of ultraviolet light. Prolonged exposure to UV rays can cause silicone to degrade, leading to discoloration, brittleness, and loss of mechanical properties. UV stabilizers help extend the lifespan of silicone products used in outdoor environments.
l Pigments and Colorants: When aesthetics are important, pigments and colorants are used to add color to silicone. These additives are carefully selected to ensure they do not compromise the material’s properties. Whether you need bright colors for consumer goods or specific shades for branding, pigments and colorants allow you to achieve the desired appearance.
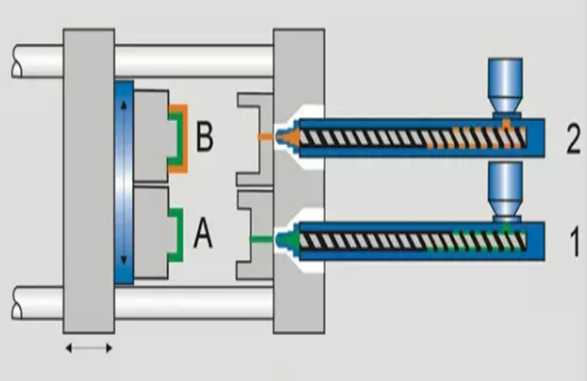
How Does Compression Molding Process?
Compression molded is a simple yet effective manufacturing process where a heated plastic material is placed into a mold cavity, then compressed under pressure to form the desired shape. This process ensures consistent, high-quality parts with minimal waste, making it ideal for both low and high-volume production runs.
l 1- Preparing the Mold
The first step is designing and preparing the mold. This includes selecting the right mold material, ensuring its dimensions match the part specifications, and preheating the mold to the required temperature. Molds are typically created based on CAD designs of the product.
l 2- Material Preparing & Loading
The material quantity must be precisely calculated to fill the mold cavity completely, avoiding both excess material and insufficient material. It often in the form of pre-measured pellets or sheets, which is carefully loaded into an open mold cavity.
l 3- Mold Closure and Heating
The mold is securely closed, and it's heated to a temperature that softens the material, making it malleable and ready for molding.
l 4- Compression and Curing
The closed mold is subjected to high pressure, causing the material to flow and fill the mold cavities. Simultaneously, the material undergoes curing or vulcanization, a chemical process that transforms it into a solid and durable product.
l 5- Cooling
After the material has taken the shape of the mold and undergone curing, the mold is cooled. Cooling solidifies the material, ensuring it maintains the desired shape and properties.
l 6- De-molding
This is a step that is undertaken after you have cured or chilled your compressed component. You are simply required to open your mold and retrieve your finished product. To extract your product, you can use a plunger-style ejector pin, which is an automated system designed to eject heavy and complex components. Alternatively, you can retrieve your finished product by hand.
l 7- Trimming
Trimming involves extracting excessive materials from your mold cavity or molded parts. This process plays a pivotal role in ensuring that your product exhibits accurate and consistent dimensions. You can manually trim your components with punching jigs supporting if needed, or exploit a specialized deburring machine such as he cryogenic de-flashing system to surgically remove unwanted materials.
l 8- Cleaning&Packing
Once you have concluded the compression molding procedure, clean your finished products as well as your compression mold. Simply use a handheld cleaner to dislodge the residual charge before applying a release agent. Do not forget to clean your mold rigorously after numerous compression cycles. After that, you can pack the final product as requested.
What is Our Custom Mold Manufacturing Capability?
Our custom contract manufacturing capabilities offer custom solutions to meet the specific needs of your business. With advanced technologies and a flexible approach, we provide high-quality, cost-effective production services for a wide range of products. Whether you need small or large-scale manufacturing, we work closely with you to ensure the final product meets your exact specifications and delivery timelines.

How to Set-up Compression Molding?
Key Parameters Control Table

What are Advantages of Compression Molding?
Compression molding has numerous worthy competitors including injection molding. However, this distinct technology continues to stand out thanks to its multitude of rewards, which include;
· Dimensional Accuracy: Compression molding heavily relies on hydraulic presses, which give you the utmost control over the molding process. This results in accurately molded products and in large-scale production, these products exhibit similar dimensions.
· Reduced Wastage: This molding process is economical on your materials meaning you can use it to mold highly-priced materials. It allows you to dispense precise volumes of charge into your mold cavities.
· Suits Large Components: If you are dealing with comparatively humongous components, compression molding will serve you well. This is because it relies on hydraulic presses or servo-electric motors capable of generating sufficient pressure.
· Cost-Effective: If your project has budgetary constraints, compression molding will be the perfect answer. Implementing it is comparatively cheaper and its minimal material wastage rewards you with relatively lower production costs.
· Smooth Surface Finish: With compression molding, supplementary finishing steps are not a necessity. This is because this molding process produces accurately measured components with smooth surfaces.
· Potential for Inserts: You can effortlessly produce an intricately designed part using compression molding. This is because compression molding allows you to insert additional reinforcement parts.
· Potential for Multi-Color Molding: When using compression molding, you can craft products or components featuring distinct colors. All you have to do is incorporate the distinct colors during material preparation.
Compression Molding Application
The compression molding process produces a wide range of rubber compression molding and plastic compression molding parts across various industries. Here are some common examples:
l Industrial parts: seals, gaskets, O-rings, bushings, Dampening components
l Electonics: Insulators, Keypads, e-cigarette filter, lamp cups, mobile and pad covers
l Houseware: floor mats, cooking tools, bakeware,ovenware,lunch boxes, pot holder, grill gloves, food trays, gloves
l Baby&Pet care: nipples, feeding-bottle, baby tableware, protect holder and covers, wristbands, pet tableware and toys
l Healthcare: Sexual products, silicone sheet mask
l Medical: fittings, breathing face masks frame, flow control valves, syringe stoppers
l Sports: body fitness tools, drinking bottles&holders, golf accessories, skiing goggles, diving masks, swimming hat, head protection
Conclusion
Silicone compression molding is a highly efficient and flexible process that produces precise and durable silicone parts, suitable for industries like automotive, medical, and consumer goods. By understanding key steps and addressing challenges such as flashing, warping, and voids, manufacturers can optimize the molding process for superior results. Proper control over parameters like pressure, temperature, and material selection ensures the production of high-quality custom silicone parts. Leveraging professional silicone compression molding services helps meet stringent performance and quality standards, making it a reliable solution for a wide range of applications.